The basic static load rating is defined as the static radial load in case of radial ball or roller bearings or axial load in case of thrust ball or roller bearings which corresponds to a total permanent deformation of the ball or roller and race at the most heavily stressed contact equal to 0 0001 times the ball.
Basic static load rating ceramic.
The static safety factor is the ratio between the basic static load rating and the maximum combined static load applied to the bearing.
Revised april 12 1989.
The basic static radial load rating is defined as the static radial load which.
The basic dynamic load rating c is used for calculating basic rating life and skf rating life for bearings that rotate under load.
The c value is defined as.
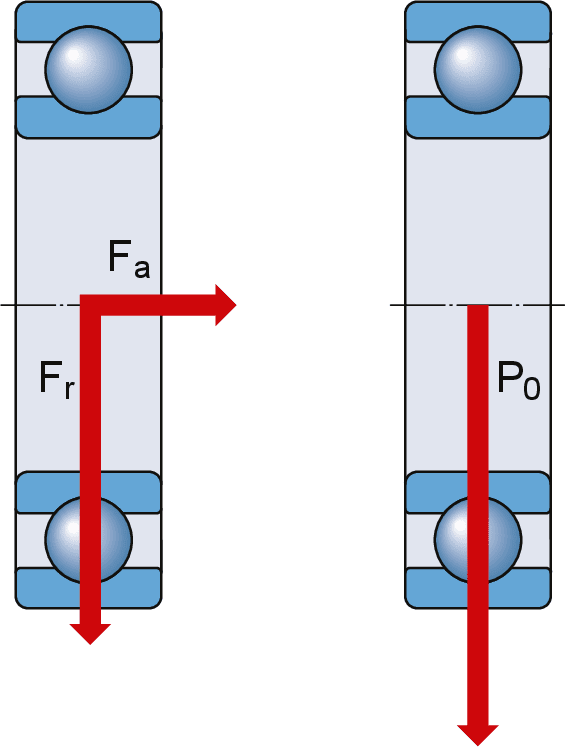
The basic static radial load rating cor applies to bearings which rotate at very slow speeds subjected to very slow oscillations or stationary under load.
24 1 kokubu higanjo kashiwara osaka 582 japan received august 25 1988.
S 0 static load safety factor.
Dynamic radial load rating the basic dynamic load rating c is used for calculations involving the selection of bearings which rotate under load.
The bearing safety factor or safety modulus f s is the ratio of the basic static load rating c or to the equivalent load p on the bearing.
It should be considered when heavy shock loading occurs to a rotating bearing.
Accepted may 8 1989 summary this.
As a rule it represents the maximum load that a spherical plain bearing or rod end can accommodate at room temperature when there is movement between the sliding contact surfaces fig.
The basic dynamic load rating c and the basic static load rating co are quoted in the bearing tables.
In the ceramic bearing therefore less deformation on the rolling elements balls or rollers generates higher stress at the contact point between the rolling element and raceway when compared to a steel bearing.
When the use conditions are normal operation a safety factor of 1 0 is typical.
It can range from 2 for smooth operating conditions with a low risk of vibrations to as high as 5 or 6 for applications that may be subjected to severe shock loads.
The basic dynamic load rating c is used together with other influencing factors to determine the basic rating life of spherical plain bearings and rod ends.
Basic static load rating.
It is assumed that the load is constant in magnitude and direction and is radial for radial.
It expresses the bearing radial load.
F s c or p.
Load ratings of ceramic bearings ceramics has a modulus of elasticity higher than that of high carbon chrome bearing steel.
All values expressed are radial ratings.