These rocks have low concentrations of large ion lithophile elements lile light rare earth elements lree volatile elements and other highly incompatible elements.
Basaltic rocks make up most of the sea floor.
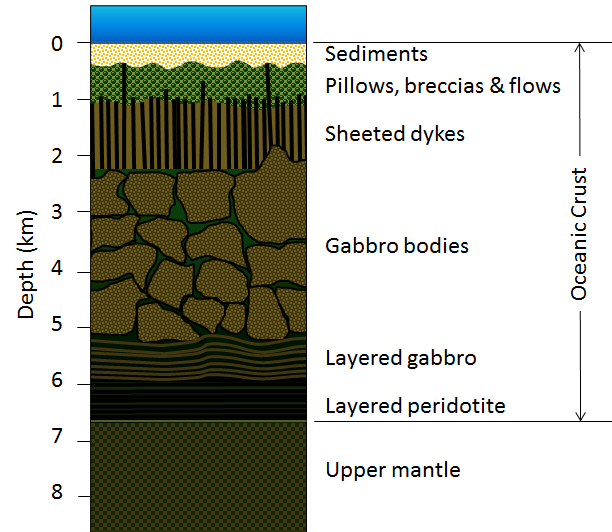
Oceanic crust is about 6 km 4 miles thick.
Have a similar texture.
The most voluminous volcanic rocks of the ocean floor are the mid oceanic ridge basalts which are derived from low potassium tholeiitic magmas.
Lava is molten rock at earth s surface.
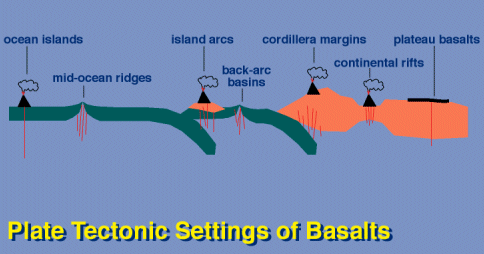
Most of earth s basalt is produced at divergent plate boundaries on the mid ocean ridge system see map.
Hydrothermal vents are common at spreading centers.
Magma is molten rock beneath earth s surface.
Intrusive igneous rocks are often characterized as coarse grained because.
Continental exceeds 70 kilometers under some mountainous regions while oceanic crust ranges from 3 to 15 kilometers.
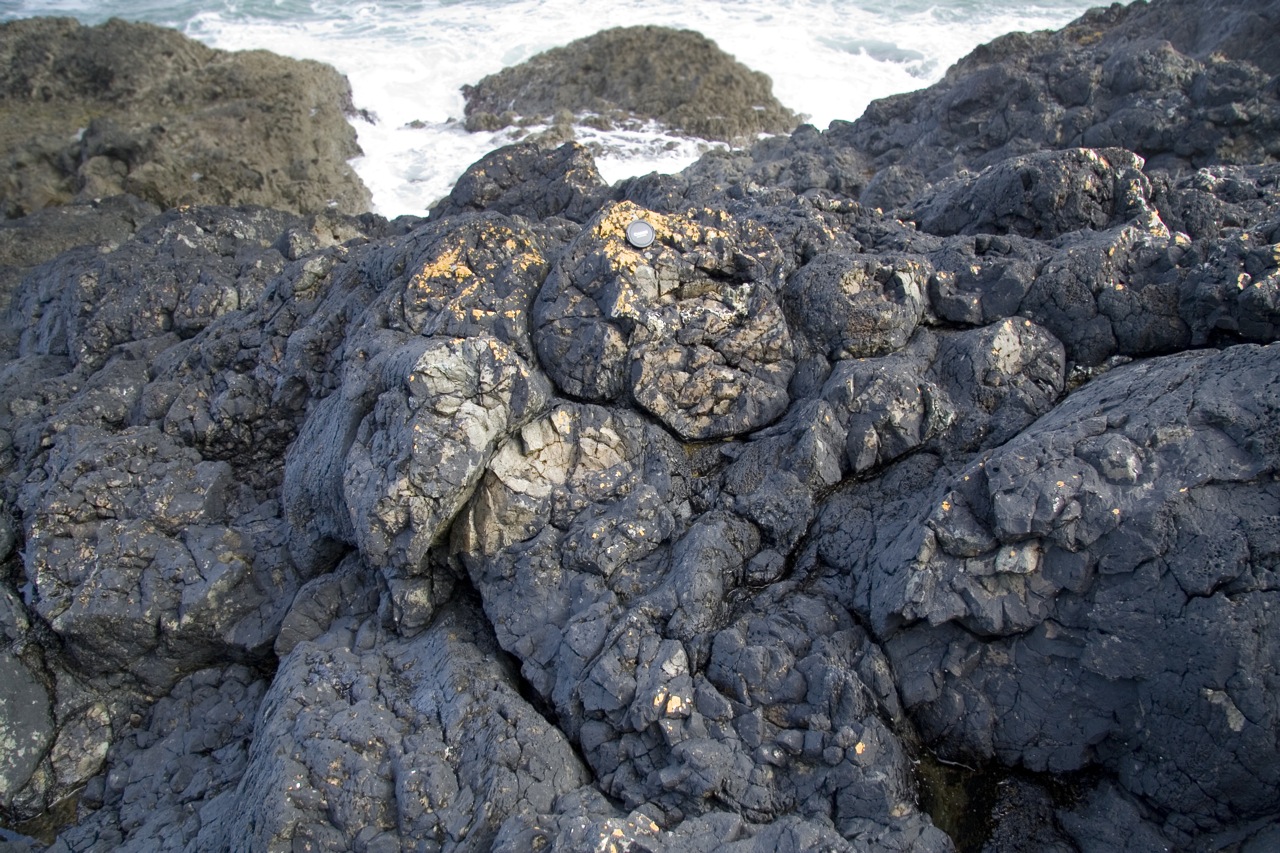
Basalt is the most common type of igneous rock and it covers the ocean floor and thus exists.
This hot rock melts as the divergent boundary pulls apart and the molten rock erupts onto the sea floor.
The topmost layer about 500 metres 1 650 feet thick includes lavas made of basalt that is rock material consisting largely of plagioclase and pyroxene oceanic crust differs from continental crust in several ways.
Most of the rocks of the earth s crust are igneous although sedimentary rocks usually cover them.
It is thinner denser younger and of different.
Basaltic rocks make up most of the sea floor a true b false.
Porosity is a measure of the volume of open space in rocks and unconsolidated geological materials such as alluvium and soils a.
How does the eruption of mount st.
The average rock density is about 2 7 g cm3 composition is comparable to the felsic igneous rock granodiorite.
How does magma differ from lava.
The density is about 3 0 g cm3 composed mainly of the igneous rock basalt.
Basalts at oceanic divergent boundaries.
Basaltic rocks make up most of the.
At a spreading center basaltic magma rises up the fractures and cools on the ocean floor to form new seabed.
Confining pressure where.
Granite and gabbro.
B ə ˈ s ɔː l t ˈ b eɪ s ɒ l t uk.
The slow cooling at depth allows large crystals to grow.
ˈ b æ s ɔː l t ˈ b æ s əl t is a mafic extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of lava rich in magnesium and iron exposed at or very near the surface of a terrestrial planet or a moon.
Basaltic rocks make up most of the sea floor.
Helens compared to a typical eruption of hawaii a kilauea volcano.
Here convection currents deliver hot rock from deep in the mantle.
Obsidian exhibits a texture.
More than 90 of all volcanic rock on earth is basalt and the eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20.